Over the past decade, silicon carbide has gained widespread use across various economic and industrial sectors due to its exceptional properties, including high wear resistance, corrosion resistance, hardness, low density, and high-temperature strength. As an advanced ceramic material, it is increasingly applied in aerospace, nuclear energy, petroleum, chemical processing, textiles, and food industries—particularly under demanding conditions such as high temperature, high speed, corrosion, vacuum, electrical insulation, non-magnetism, and dry friction.
1. Magnetic Pump Components
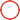
With the rapid growth of fine chemical production and stricter environmental standards such as ISO 14000, which aim to eliminate leakage and emissions, there is a rising demand for reliable transport of corrosive fluids. Magnetic pumps, which use static sealing instead of dynamic sealing methods like mechanical or packing seals, offer minimal leakage, high reliability, and extended service life—typically maintenance-free for 5–8 years. This places stringent requirements on shaft system materials, which must be wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and leak-proof. Pressureless sintered silicon carbide has emerged as the ideal material for such components.
![]()
Magnetic Pump Components
2. Mechanical Seals
Pressureless sintered silicon carbide offers excellent corrosion resistance, high strength and hardness, wear resistance, low friction coefficient, oxidation resistance, minimal high-temperature creep, and superior thermal stability. Its fine, dense microstructure with low free silicon and carbon content makes it especially suitable for high-purity, ultra-clean, and fine chemical applications. When precision-finished, it exhibits a lower friction coefficient than alumina ceramics or cemented carbide, enabling high PV values and reliable performance in strong acid, alkali, and other corrosive media. Our company's silicon carbide features high density (3.10–3.20 g/cm³) and hardness (HRA 94), and we mass-produce complex seal ring geometries including flat, single-step, and multi-step designs.
![]()
Presureless sintered SIC bushing bearing parts for pump
3. Nozzles
In sandblasting applications, pressureless sintered silicon carbide has become the second most widely used material after boron carbide, replacing both cemented carbide and alumina ceramics. Although alumina nozzles are inexpensive, their low hardness and poor wear resistance limit them to light-duty use. Silicon carbide nozzles last 4–7 times longer than alumina and are increasingly used as a high-performance alternative to cemented carbide. Additionally, silicon carbide is widely adopted in other components such as ceramic ball valve cores, plate heat exchanger sheets, and military ceramic armor, with growing popularity across advanced industrial and defense applications.
![]()
Presureless sintered SIC nozzle
Additionally, silicon carbide is widely adopted in other components such as ceramic ball valve cores, plate heat exchanger sheets, and military ceramic armor, with growing popularity across advanced industrial and defense applications.